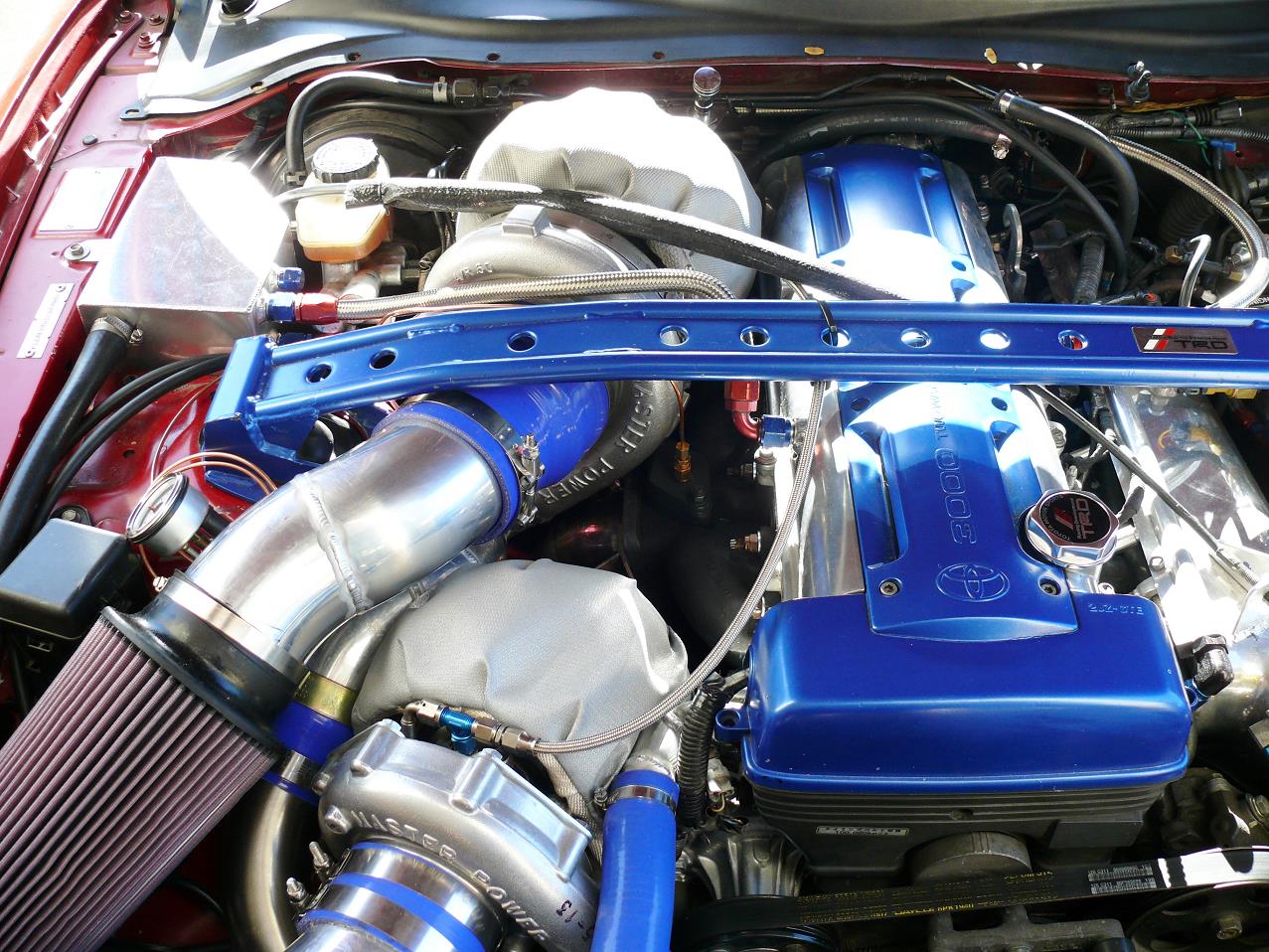


In this case, multiple similarly sized turbochargers are used in sequence, but constantly operating.
#Compound sequential turbo serial
Serial turbocharging is where the turbochargers are connected in series with the output of the first turbocharger then being further compressed by the second turbocharger and in some cases powering the larger turbine.Ī sequential turbo can also be of use to a system where the output pressure must be greater than can be provided by a single turbo, commonly called a compound twin-turbo system. The first production car to use sequential turbocharging was the 1986-1988 Porsche 959, which used sequential twin-turbos on its flat-six engine. Then at high RPM, all of the exhaust gases are directed to the secondary turbocharger, so that it can provide the boost required by the engine at high RPM. As RPM increases, a small amount of exhaust gas is fed to the larger ("secondary") turbocharger, to bring it up to operating speed. The system is arranged so that a small ("primary") turbocharger is active while the engine is operating at low RPM, which reduces the boost threshold (RPM at which effective boost is provided) and turbo lag. Therefore, sequential turbocharger systems provide a way to decrease turbo lag without compromising power output at high RPM.
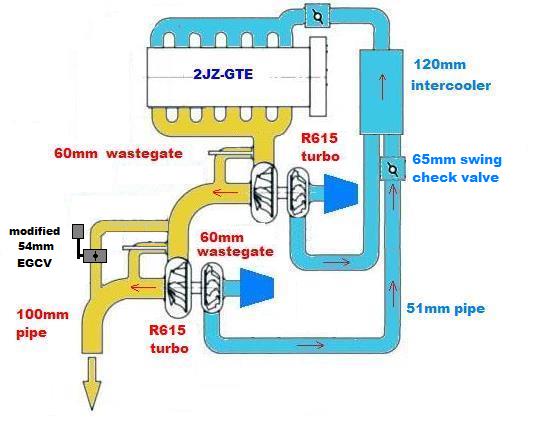
On the other hand, smaller turbos are effective at low RPM (when there is less kinetic energy present in the exhaust gases) but are unable to provide the quantity of compressed intake gases required at higher RPM. This system is intended to overcome the limitation of large turbochargers providing insufficient boost at low RPM. Sequential turbocharging refer to a set-up in which the engine uses one turbocharger for lower engine speeds, and a second or both turbochargers at higher engine speeds. The 1981-1994 Maserati Biturbo was the first production car to use twin-turbochargers. V engines and flat engines) use of parallel twin-turbos can also simplify the exhaust system. On engines with multiple cylinder banks (e.g. The aim of using parallel twin-turbos is to reduce turbo lag by being able to use smaller turbochargers than if a single turbocharger was used for the engine. For four-cylinder engines and straight-six engines, both turbochargers can be mounted to a single exhaust manifold. In this case, each turbocharger is fed exhaust gases by a separate exhaust manifold. Parallel configurations are well suited to V6 and V8 engines since each turbocharger can be assigned to one cylinder bank, reducing the amount of exhaust piping needed. Some designs combine the intake charge from each turbocharger into a single intake manifold, while others use a separate intake manifold for each turbocharger. Porsche 935 flat-six engine with parallel twin-turbosĪ parallel configuration refers to using two equally-sized turbochargers which each receive half of the exhaust gases.
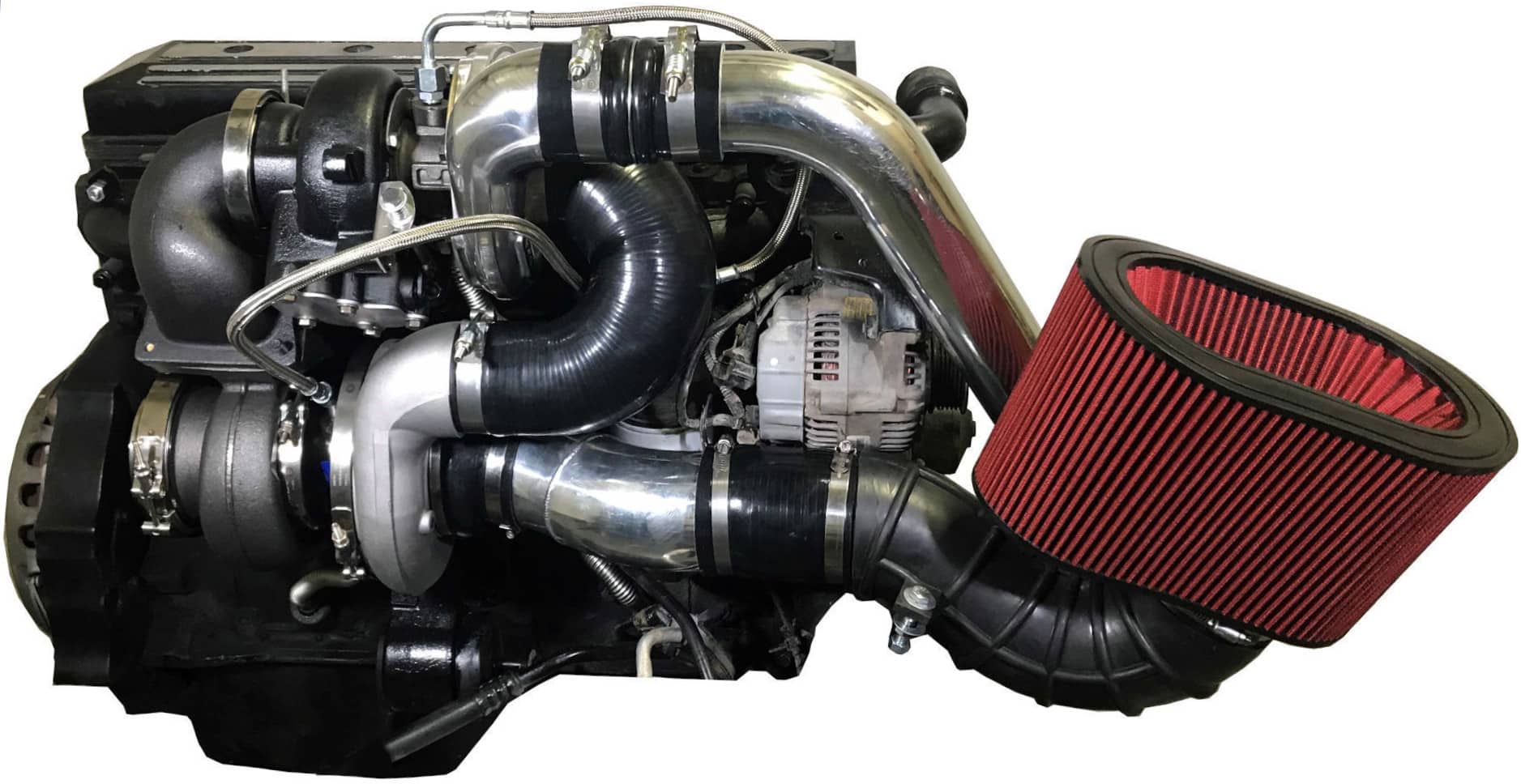
These can be applied to any of the five types of compressor setups (which theoretically could have 15 different setups): There are three types of turbine setups used for twin-turbo setups: The two turbochargers can either be matching or different sizes. The most common layout features two identical or mirrored turbochargers in parallel, each processing half of a V engine's produced exhaust through independent piping. Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case of a direct-injection engine). ( August 2023) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) Statements consisting only of original research should be removed.

Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. This article possibly contains original research.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
